The Colosseum, standing tall amidst the bustling streets of Rome, is more than just a monument. It is a living testament to the ingenuity and power of the Roman Empire. This ancient amphitheater, despite facing devastating earthquakes, remains a timeless icon of Roman architecture and a must-see attraction for any visitor to the Eternal City.

A Masterpiece of Design and Engineering
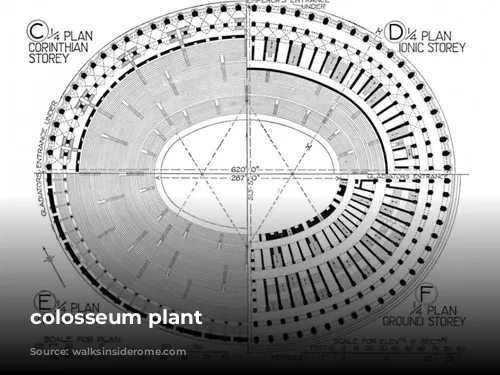
The Colosseum’s impressive size and elliptical shape are instantly recognizable. Built entirely from concrete and stone, its vaults and arches create a harmonious and robust structure. The columns, which connect the tiers of the Colosseum, are a testament to Roman admiration for Greek architecture, featuring three distinct styles: Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian. Each style boasts its own unique decorative elements, ranging from simple designs to intricate carvings of acanthus leaves.

The Colosseum: A Monument to Roman Engineering
The Colosseum stands as a prime example of Roman engineering prowess, utilizing innovative construction techniques to build a grandiose structure. Travertine, a limestone abundant in the region, was a key material, complemented by concrete, brick, and stone. The Romans also employed tuff, a volcanic rock, available in various colors, to enhance the building’s visual appeal. To hold these materials together, iron and bronze clamps were used, acting as giant paper clips to bind the massive structure. While not evident today, the Colosseum’s seating, particularly in the first three rows, was originally adorned with marble, adding to the visual hierarchy that reflected the social classes of ancient Rome.

A Glimpse into Roman Life
The Colosseum’s underground area, known as the Hypogeum, comprised a network of tunnels and elevators that served as a backstage for the gladiators, animals, and props. This sophisticated system allowed for the seamless flow of performances in the arena.
The Colosseum played a crucial role in Roman social life, hosting gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, and public events. The amphitheater’s elliptical arena and tiers of seating were designed to separate spectators according to their social status, creating a visible hierarchy that mirrored the inequalities of ancient Roman society. The Podium, closest to the arena, was reserved for the Emperor, priests, and senators, while the upper tiers were occupied by common citizens and, at the very top, women.
A Monument to Roman Power and Glory
The Colosseum’s seating capacity of 85,000 spectators is a testament to its grandeur and the power of the Roman Empire. Its magnificent design, a fusion of arches, vaults, and architectural styles, makes it a masterpiece of Roman engineering and a symbol of Roman civilization.

Explore the Colosseum with Walks Inside Rome
For those who want to delve deeper into the secrets of the Colosseum, Walks Inside Rome offers guided tours that will unravel its architectural wonders. Join a tour and step through the Gladiator’s Gate, experiencing the thrill of the arena and gaining invaluable insights into this iconic monument.


