The Roman Empire wasn’t built overnight. It was a tapestry woven with countless threads, each representing a conquest, a victory, and a new piece of territory added to the expanding empire. One of the most crucial threads in this tapestry was the Roman conquest of Jerusalem. This event, fueled by the ambition of Pompey the Great, set the stage for the birth of Christianity and the eventual spread of Roman civilization across the Mediterranean.
The Rise of Pompey and the Fall of Jerusalem
Pompey’s military prowess wasn’t just a matter of talent; fate played a crucial role in his rise to power. After conquering Mithridates VI in the Third Mithridatic War, Pompey was awarded control of the strategically vital province of Syria. This gave him access to the Eastern Mediterranean, a region brimming with riches and power.
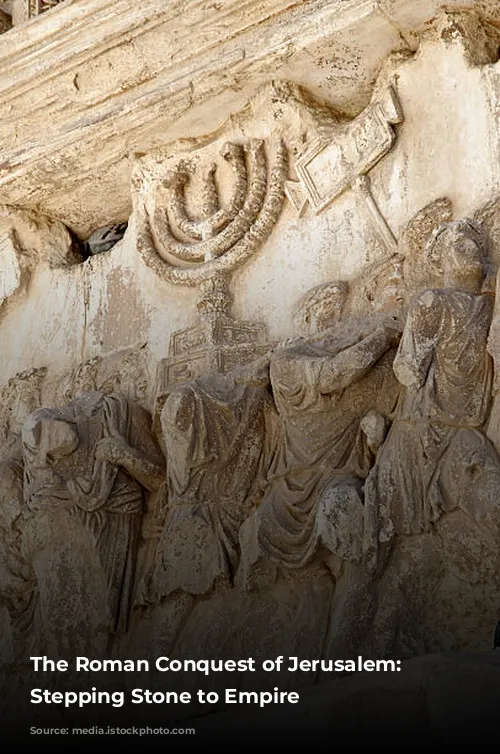
With eleven legions and 600 war galleys at his command, Pompey became a force to be reckoned with. His influence was so immense that he could practically dictate his own destiny. It was this power that led him to Jerusalem in 63 BC. A combination of favorable circumstances and a bribe allowed Pompey to seize control of the Holy City.
The Roman grip on Jerusalem solidified further in 37 BC when Mark Antony aided the future King Herod in securing the throne of Judea. This set the stage for the birth of Christ and the events that would unfold in the future, including the crucifixion of Jesus at the hands of the Roman governor Pontius Pilate.
A Sea of Civilization: The Roman Influence
The Roman conquest wasn’t just about military dominance; it was a catalyst for the spread of civilization across the Mediterranean. After the death of Antony and Cleopatra in 31 BC, Octavian (later known as Emperor Augustus Caesar) became the undisputed ruler of the entire Mediterranean coastline.
Roman fleets of warships patrolled the waters, connecting the different parts of the empire. These ships, originating from fortified ports like Portus Julius and Messina, carried with them the essence of Roman civilization, spreading its influence across the known world.
However, the Roman empire wasn’t a monolith. Their conquests brought them into contact with diverse cultures— Greek, Persian, Egyptian, and Jerusalemite — all of which left their mark on Rome. This can be seen in the architecture, art, and culture of Roman cities along the Amalfi Coast, Sicily, and Sardinia.
A Legacy in Stone: Exploring Roman History
The Vatican Museums house a treasure trove of ancient Roman artifacts, offering a glimpse into the lives of Pompey, Julius Caesar, and the empire they built. Visitors can delve into the history of Ostia, a vital marshaling ground and seaport that served as the launchpad for many Roman conquests. Today, Ostia Antica, an archeological site, reveals the remnants of this once-powerful military center.
For those seeking insights into the history of Jerusalem before Roman occupation, the “Antiquities of the Ancient Near East” exhibit at the Vatican Museums is a must-visit. It houses the Dead Sea Scrolls, alongside other ancient Palestinian and Egyptian artifacts. The exhibit also showcases fascinating objects from the necropolis of Jericho.
As you explore the Vatican Museums, take a moment to reflect on the legacy of the Roman Empire. Its influence can be seen in every corner of the world, from the ancient ruins of Ostia to the bustling streets of modern cities. The Roman conquest of Jerusalem was not just a military victory; it was a turning point in history, shaping the course of Western civilization as we know it.
The Legacy of the Roman Empire: A Continued Journey
The Roman Empire’s legacy lives on. As the Lenten season approaches, we will delve into the origins of Ash Wednesday and explore the evolution of Christianity through Italian influence. Stay tuned for our upcoming articles, starting next week.
Join us as we continue to explore the fascinating history of the Roman Empire and its impact on the world.